UpSampling
In many cases including image segmentation, a model consists of downsampling and upsampling parts and the latter restore the feature map to the input sized image. There are two types of upsampling using torch: UpSampling, ConvTranspose2D.
1. UpSampling
Simply scale up of an image by using nearest neighbor or bilinear upsampling; a simple interpolation.
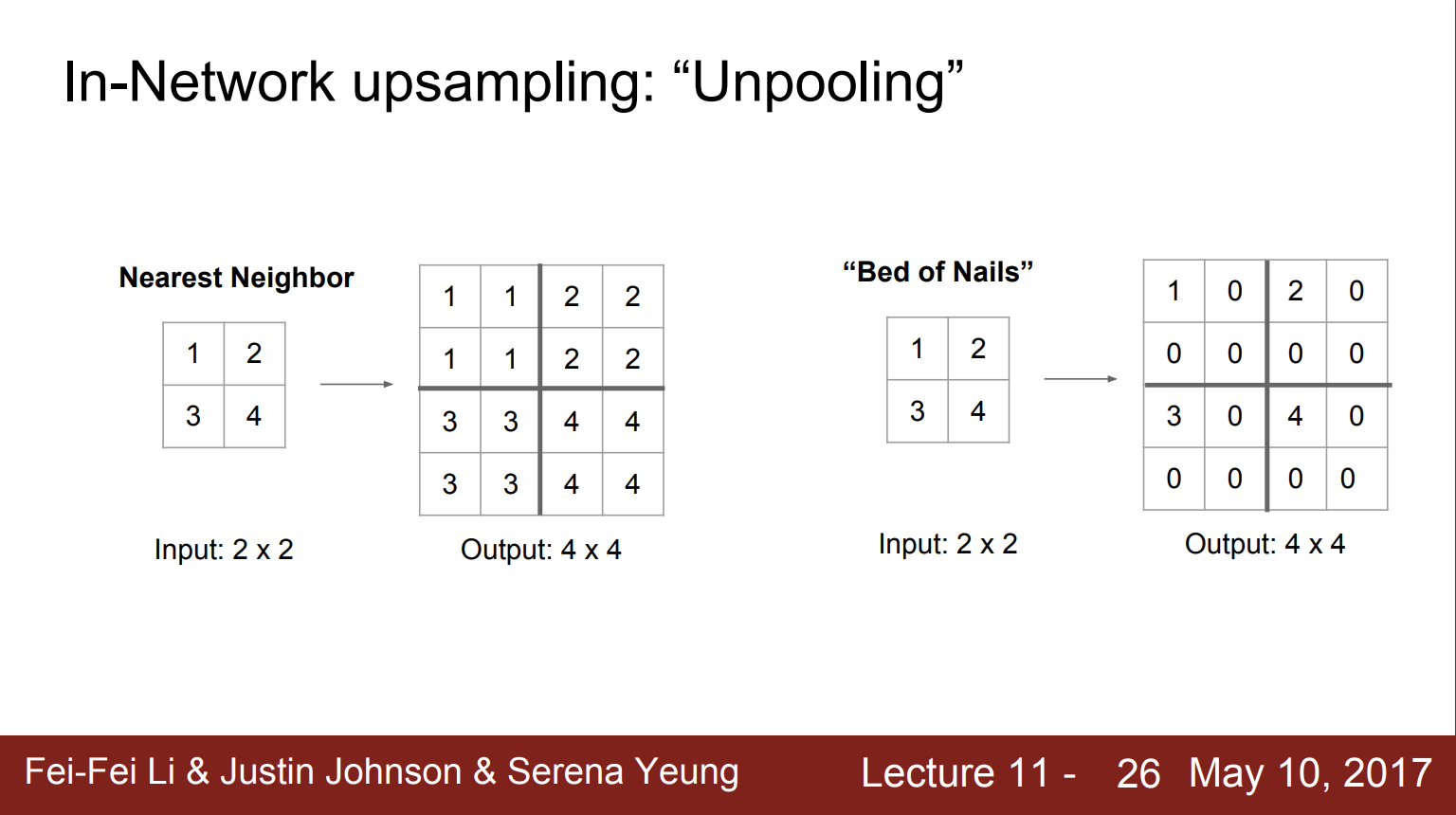
The above picture describes how to reconstruct 2x2 sized image into 4x4.
Examples (torch):
input = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float32).view(1,1,2,2)
m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode="nearest")
2. ConvTranpose2D
Just think of the convolution process and tranpose. Compared to the above upsamling method, the ConvTransposed2D trains the upsampling filter.
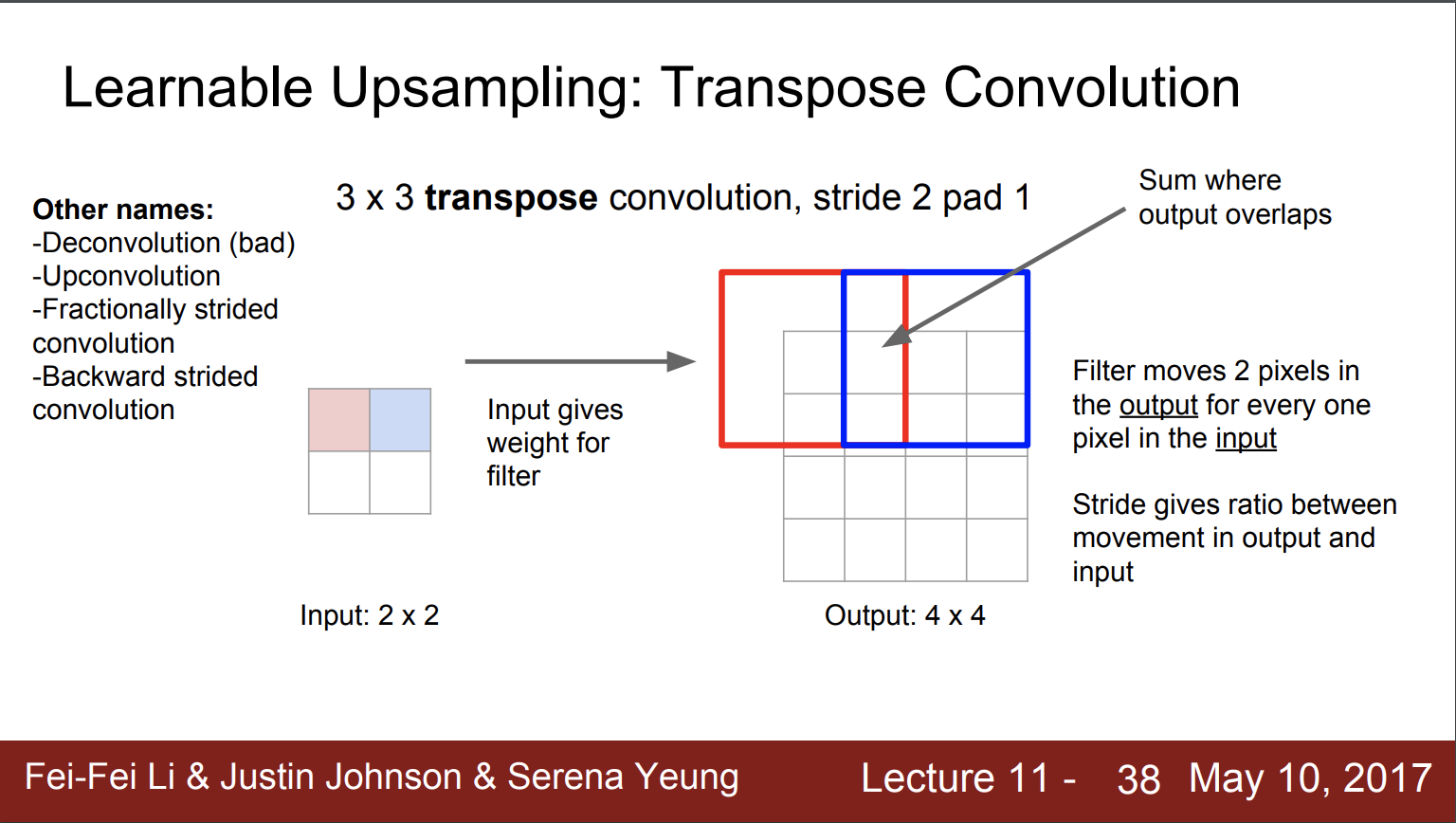
input = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 100)
m = nn.ConvTranspose2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2))
Reference
- http://cs231n.stanford.edu/slides/2017/cs231n_2017_lecture11.pdf
- https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Upsample.html
- https://towardsdatascience.com/is-the-transposed-convolution-layer-and-convolution-layer-the-same-thing-8655b751c3a1
