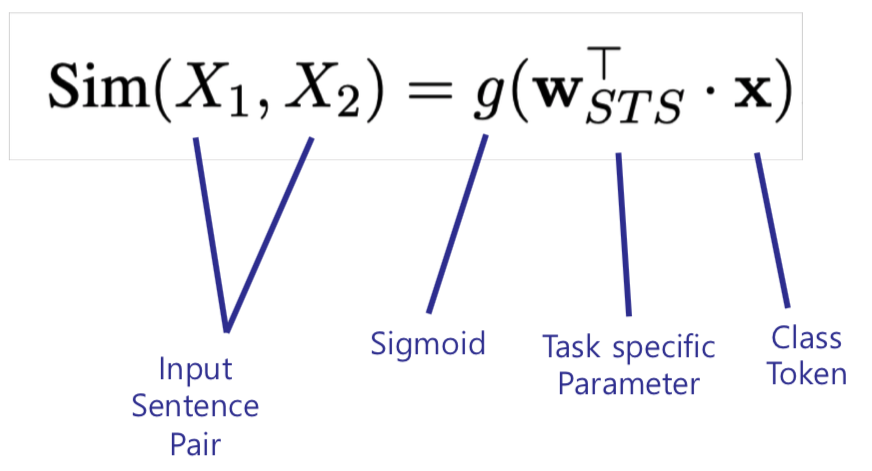Multi-task Learning & MT-DNN
In this posting, I will talk about Multi-Task Learning (MTL) briefly and then deal with the NLP model named MT-DNN.
Multi-task Learning
1. Concept
Multi-Task Learning is a learning paradigm that seeks to improve the overall performance of all task performance by simultaneously learning related tasks. In particular, we use MTL a lot when we want to learn multiple Supervised tasks through a single model. WHY? MTL starts with the idea that people who are good at soccer can run better than ordinary people. In other words, learning models with the assumption that knowledge learned between tasks can influence each other to improve performance.
2. Pros & Cons
- Pros :
1) Can utilize Supervised data more efficiently : Since the Supervised Dataset has a limited amount under Task, performance is significantly reduced when data volumes are low. However, we can use massive Supervised data if we gather them all together and utilize in MTL.
2) Regularization : Since we implement multiple tasks simultaneously, it can have a regularization effect so that the model is not overfitted on a particular task.
3) Computational Efficiency
- Cons :
1) Negative Transfer : There may be tasks that adversely affect other tasks.
2) Difficulty in Task Balancing : If the learning difficulty varies significantly from task to task, it does not converge or is not powerful.
3. Sharing methods
Also, there are 2 kinds of Sharing in MTL - Soft sharing & Hard sharing
-
Soft Sharing : Starts from different models and share information in-between.

-
Hard Sharing : Starts with the same root model and later learns each representation.

4. Combining Loss
How to Combine Loss ? : The tricky part of MTL is that how can we define a single loss function for multiple tasks. While a single task has a well defined loss function, with multiple tasks come multiple losses. Simply summing all losses may not be a good idea if the losses’ scales from various tasks are of great difference.
One way to solve this is to use uncertainty to weigh losses in MTL. We can implement this by learning another noise parameter that is integrated in the loss function for each task. To learn more about this method, read the paper : https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07115
Multi-Lable (x) & Multi-Task (o)
** CAUTION : If all tasks are composed of the same training data, the model is a simple multi-label learning or multi-output regression rather than a MTL, so each task consists of a different training set in MTL.
MT-DNN
1. Concept
MT-DNN has a structure similar to BERT, but it is characterized by handling multiple tasks at once, i.e. use MTL. MT-DNN utilizes 9 tasks from GLUE for multi-task learning, which can be categorized into 4 classes.
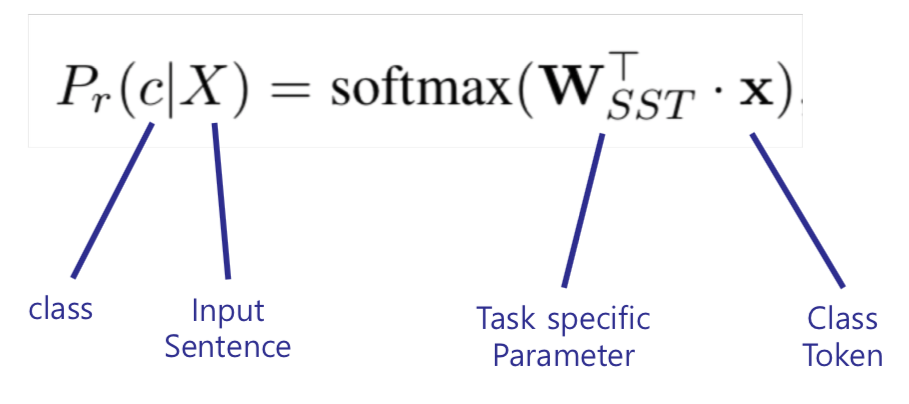
1) Single Sentence Classification : Task to classify a class of sentences when given a single sentence
2) Text Similarity : Regression task to predict similarity scores given a pair of sentences
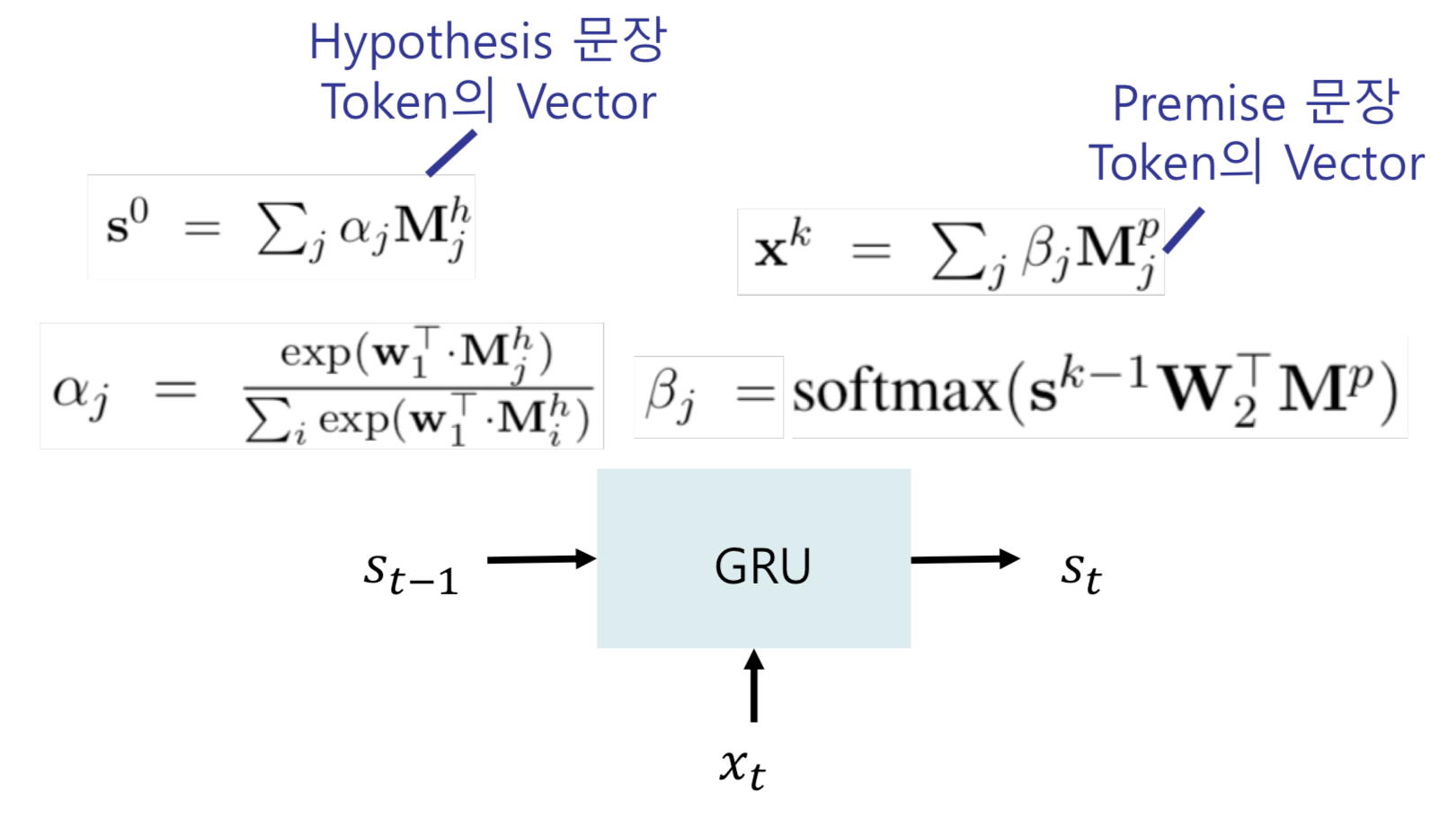
3) Pairwise Text Classification : Task to classify the relationship of a sentence when given a pair of sentences
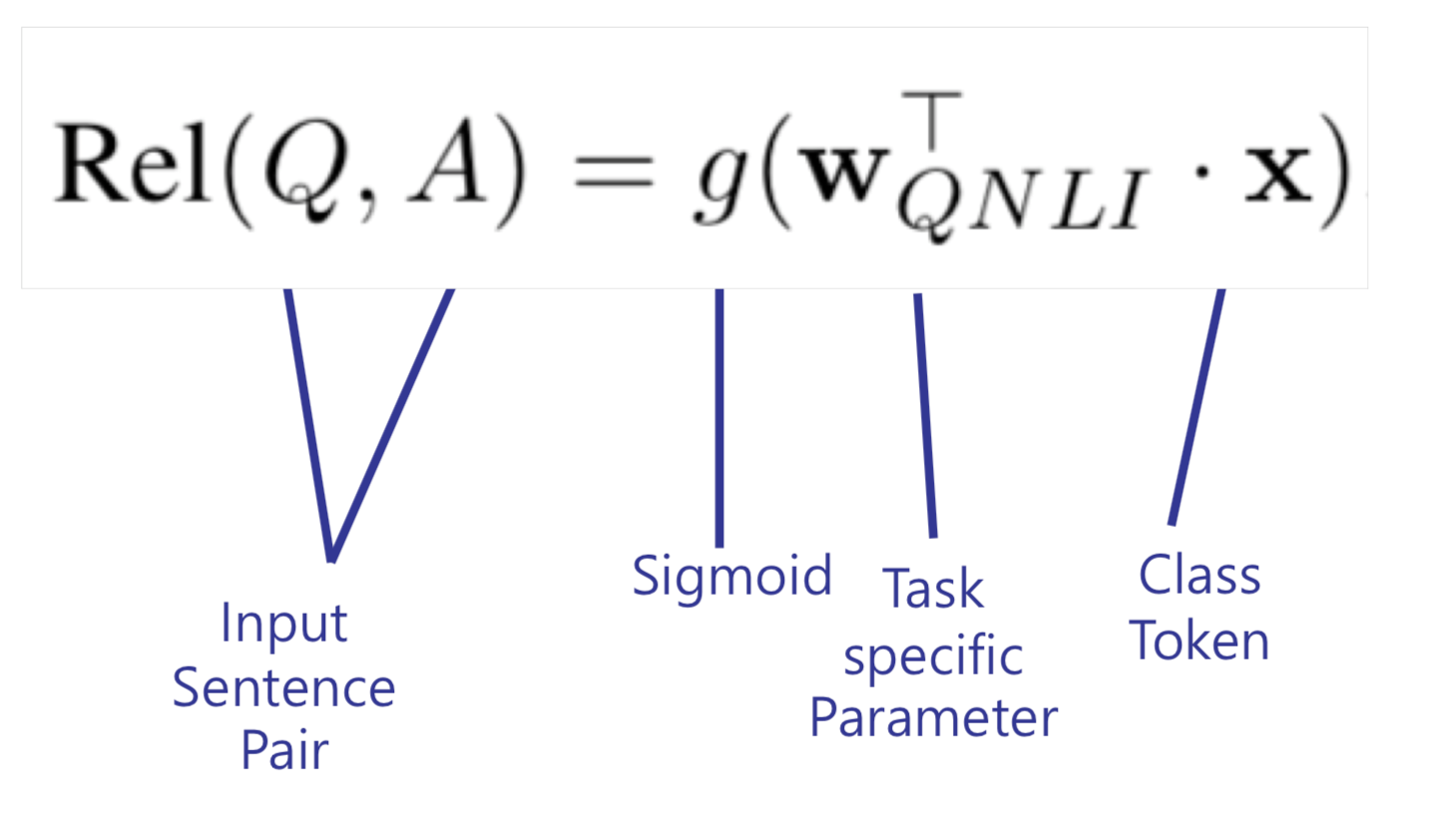
4) Relevance Ranking : Task to find the correct sentence in the question sentence and paragraphs through Ranking
2. Model Architecture
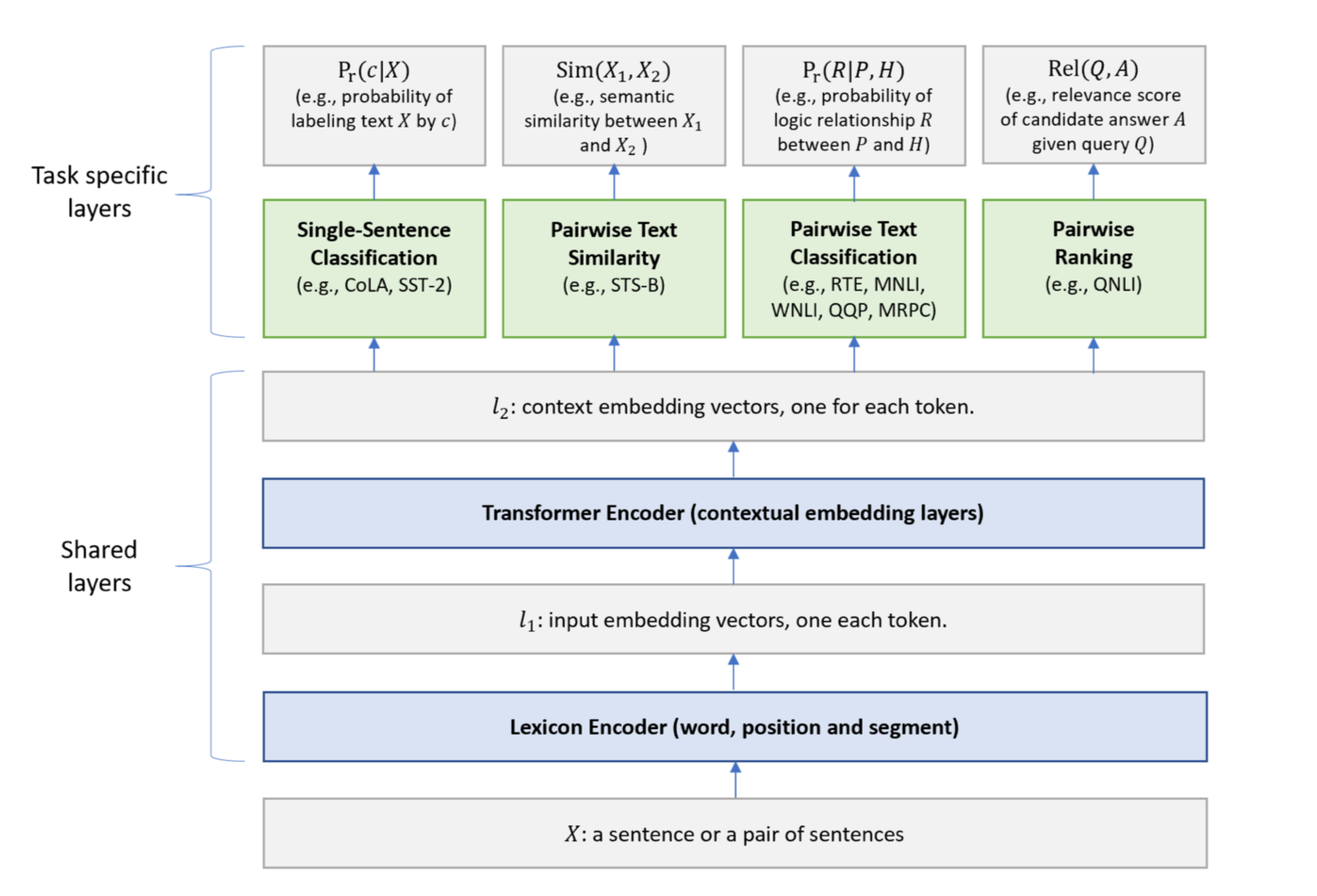
Recall the BERT that we learned earlier. Shared Layer part of MT-DNN is the same as BERT, but Task Specific Layer is configured in some ways different from those of BERT. Task specific layers can be classified into 4 types which were mentioned above, and the model can be named Multi-Task (MT) since it performs multiple tasks simultaneously.
During model training, data from a particular task is randomly drawn to batch. Shared layers continue to be learned, but Task Specific Layer is only learned from the randomly chosen data allocated to each task. (One Task Specific Layer exists for each task, and the Loss Function is configured for the task.)
The purpose of this posting is to learn about the structure of MTL and MT-DNN, so we will not look into the analysis method by task in detail.
Here are the 4 brief explanation about solving 4 tasks :
1) Single-Sentence Classification :
2) Text Similarity :
3) Pairwise Text Classification : Use Stochastic Answer Network (SAN) -> Use RNN to predict the classification results at each time step and obtain the combination of the results. In other words, predicting the results by reasoning them through multiple predictions rather than predicting the classification results once.
4) Relevance Ranking :
3. Evaluation results
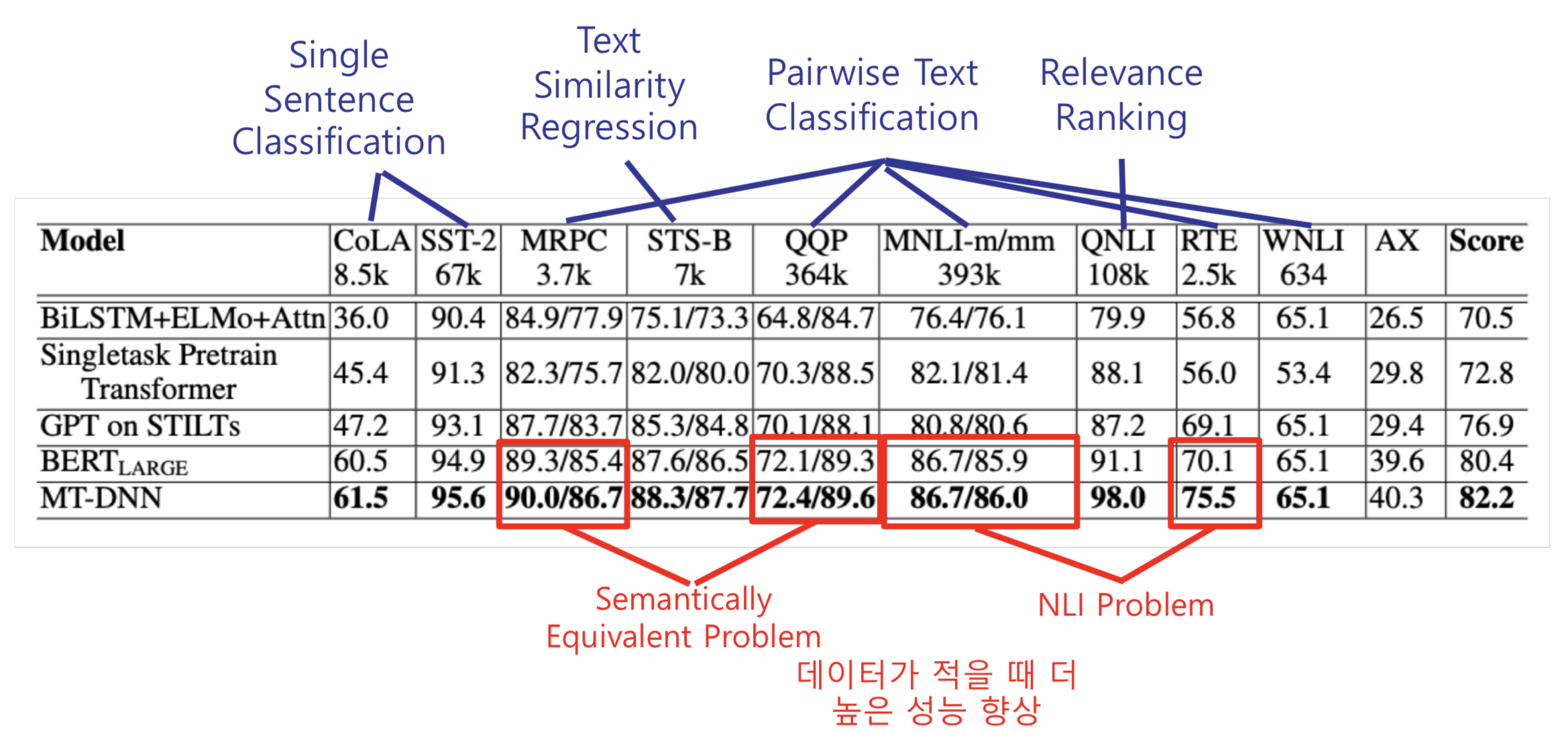
The results of MT-DNN show better results than existing BERT models on 8 of the 9 tasks of GLUE. In particular, for tasks with smaller datasets, performance improvements were higher. This shows that MT-DNN performance is much higher when fine tuning with a small amount of data due to the advantages of MTL mentioned earlier.
Reference :
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.05098v1.pdf
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1007379606734
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07115
- https://mapadubak.tistory.com/40
- https://feedforward.github.io/blog/multi-task-learning-using-uncertainty/
- https://tmaxai.github.io/post/mt-dnn/
- https://towardsdatascience.com/deep-multi-task-learning-3-lessons-learned-7d0193d71fd6