From previous post, we learn that objection detection = classification + localization to multiple objects. Today we are going to cover some important papers about object detection using deep learning architecture.
One-Stage vs Two-Stage
To begin with, there are two types of objection detection model: One-stage model, two-stage model. Two-stage model is contructed as follow:
Stage 1: Find RoI(Region of Interest)
Stage 2: Classification
On the other hand, one-stage model process those two steps at once.
R-CNN, fast R-CNN and faster R-CNN are prime examples of the two staged model and they are, as you might notice, much slower but precise than the one-stage model. One-stage model is much faster but less precise. Thus, you need to consider the aim of your project - efficiency? accuracy? - to decide which model to start with.
What is R-CNN? the first deep learning approach to object detection?
R-CNN, the first approach to apply deep learning architecture to object detection, is proposed by this paper. The overview is:
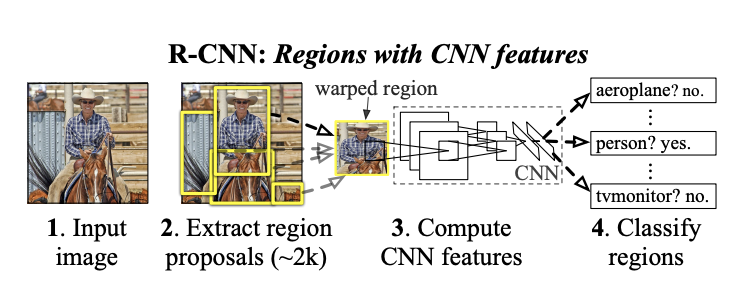
R-CNN consists of three modules:
- generate category-independent region proposals
- selective search to extract 2k candidate regions
- CNN as a feature extractor from each region
- warp all pixels in a tight box as an input (to a compatible size with the CNN)
- pretrain CNN using ImageNet
- fine tuning: N+1 (class + background) output by last FC layer
- class-specific SVM as a classifier
What is selective search?
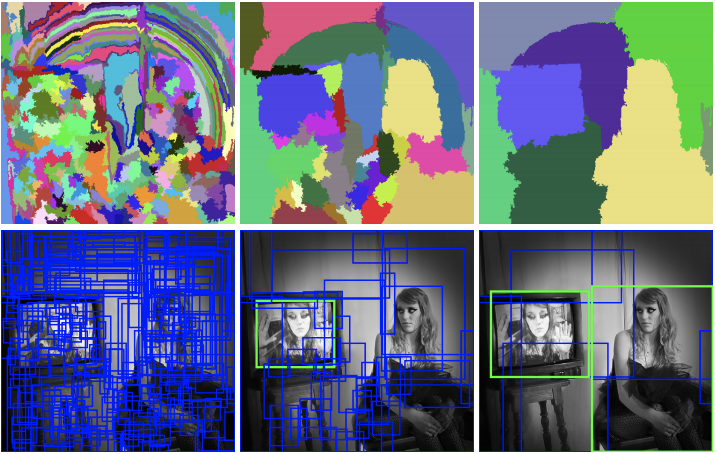

Briefly, as you can see in the left picture, it initializes boxes with various width and height. Then, calculate similarties between boxes to group similar ones together through the greedy algorithm (middle picture). Repeat grouping until a single region is left. This is called bottom-up approach, which is a popular method to segmentation.
Why replacing softmax with SVM?
When R-CNN was first proposed, fine-tuning data is so limited that SVM performed better in this paper.
When testing:
We will get scores for each feature vector for each class as the output of the SVM classifier. Then take a greedy non-maximum suppression, which calculates IOU(intersection over union) of the ground truth (region) and region proposal from selective search and rejects region if its IOU is less than a threshold (generally 0.5). This IOU measure helps to resolve situations when an object partially appears, which is vague to lable.
However, R-CNN has disadvantages:
- computational cost for SVM and bounding-box regressor training
- too slow
Next time, we will talk about Fast R-CNN and check how it improves model performance.
Reference
- https://towardsdatascience.com/step-by-step-r-cnn-implementation-from-scratch-in-python-e97101ccde55
-
Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation
- Selective Search for Object Recognition
