Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality
Goal
To improve the Vector Representation Quality of Skip-gram (one of the Word2Vec method).
There are 4 ways to improve representation quality and computational efficiency.
Method 1 - Phrasing
The problem with traditional word-based learning is that it is impossible to interpret the phrase, which consists of two words like ‘Boston Globe’ and whose meaning is not related at all to the two words.
Another familiar example could be ‘New York Times’ :
-> New York (city) + Times = New York Times (magazine) ??
Existing methods is not good at representing these kinds of Idiomatic phrases. To address these problems, in this paper, authors propose to view each phrase itself as an independent token. That is, they tried to train large amounts of phrases based on data.
The procedure is as follows :
-
Find words that appear frequently, but each one does not appear well by calculating the score.
-
Score :
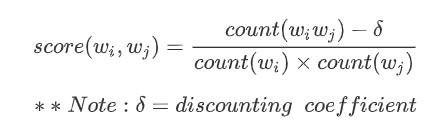
-> If you don’t want to make infrequent words to phrases, then control the parameter delta to accomplish that.
-
If the score of certain words is higher than the threshold, which is already determined in advance, then regard them as phrase.
-
Decrease the threshold as the trial goes, to find longer phrases consist of more than 3 words. (e.g. New York Times)
Method 2 - Subsampling
Subsampling is a method used when there are many populations.
- 1) Divide the data into groups
- 2) Take samples from each group
Using subsampling, we can only use samples, not the whole data.
Then, WHY do we need this? For what?
In English, there are some words that appear frequently but do not contain much information than those who appear less - e.g. ‘in’, ‘the’, ‘a’ etc. Since they do not play important role in a sentence or document, vector representation of these words does not change much no matter how hard we train.
Therefore, Subsampling allows us to filter out insignificant words and increase the computational efficiency (time reduction) without losing accuracy. Surprising fact is that, the authors figure out accuracy of the model improved as they conducted subsampling based on phrases (Method 1 mentioned above).
Then, how can we decide whether a word appears frequently or not?
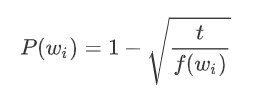
As certain word w_i appears frequently, f(w_i) increases, thus the value of P(w_i) increases, too. t is threshold. If P(w_i) > t , we subsample the word w_i.
Method 3 - Negative Sampling
The main idea of Negative sampling is that we don’t need to use all words including the ones which are not closely related to the target words. Negative sampling is a simplified variant of **Noise contrastive estimation (NCE) **.
First of all, what is NCE ? For detailed explanation, check here : http://incredible.ai/nlp/2017/11/25/Word2Vec-Noise-Constrastive-Estimation/
-> Summary: It is commonly used when the number of words is high, and NCE allows the problem to be replaced by a binary classification problem that distinguishes between (samples obtained from real distributions) and (samples obtained from artificial noise distributions). After assigning noise distribution and true distribution, update the parameters during training to increase the accuracy of vector presentation. Use (binary) cross entropy as the loss to handle binary forms.
WHY do we need negative sampling? The reason is to reduce computation significantly. If you want to derive vector representation using the whole word without pulling the negative samples, you need to compute the softmax, which requires you to calculate inner product between the target word and all the other words, then take the exponential again.
HUGE COMPUTATION !!
To avoid this, the authors suggest to apply negative sampling, which enables us to use some words (NOT all) when calculating softmax value.
Procedure :
-
Draw 5 to 20 negative samples that do not appear within the window size you specify.
-
Objective function :
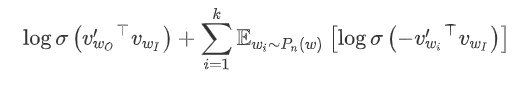
-
Negative sample formula :
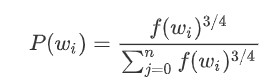
-
Combine Positive samples & Negative samples, and then compute softmax.
Note that the exponential part of f(w_i) should be smaller than 1 to increase the probability of choosing rare words as negative samples (compared to frequently appearing ones).
Note: The difference between NCE and NEG (Negative sampling) is whether the numerical probability itself is necessary or not.
Method 4 - Hierarchical Softmax
This can work as an alternative method of Negative sampling. The hierarchical softmax method is advantageous for words that do not appear frequently, and negative sampling is more suitable for words that appear frequently.
Hierarchical Softmax begin with the idea of obtaining probabilities without calculating normalizing constant which is needed when computing softmax value.
The equation below tells us the probability of choosing which direction to move (left or right).
-> LEFT : +1 / RIGHT : -1
Note : Thanks to sigmoid, we don’t need to normalize the above equation. It is already normalized.
- Ex) 'I live in Seoul and like data analysis' :

Note that the target word in this example is ‘Seoul’ and window size is 1. When the vector of the word ‘Seoul’ comes in, each node is multiplied by its corresponding weights, and then it enters the sigmoid function and comes out as a probability. Hierarchical Softmax learns weights from this tree structure, and because it is a binary classification, it has a calculation of log_2(word count) -> COMPUTATION REDUCTION.
Reference :
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1310.4546
- http://incredible.ai/nlp/2017/11/25/Word2Vec-Noise-Constrastive-Estimation/
- https://yunmap.tistory.com/entry/%EB%85%BC%EB%AC%B8-Distributed-Representations-of-Words-and-Phrases-and-their-Compositionality-Tomas-Mikolov
- https://dalpo0814.tistory.com/7
- https://analysisbugs.tistory.com/184
- https://pythonkim.tistory.com/92
- https://ratsgo.github.io/from%20frequency%20to%20semantics/2017/03/30/word2vec/

